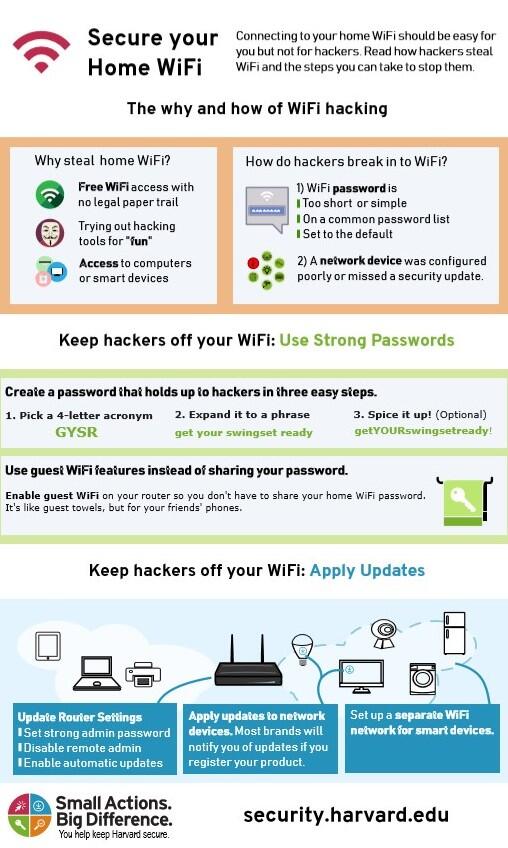
Digital Twin Technology Use Cases in Industry: Turning Data into Actionable Intelligence
Digital twin technology is revolutionizing how industries design, monitor, and improve physical systems by creating virtual replicas of real-world assets. These digital counterparts enable real-time simulation, predictive analytics, and data-driven decision-making, offering businesses a powerful tool to boost efficiency, reduce risk, and optimize performance. From manufacturing floors to smart cities and beyond, digital twin technology use cases in industry are expanding rapidly. If you’re a business leader, engineer, or tech strategist looking to stay ahead in the era of intelligent systems, understanding where and how digital twins are applied is critical.
Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing: Catch Failures Before They Happen
One of the most impactful applications of digital twin technology is in manufacturing, where equipment downtime can be costly. By simulating the behavior of machines in real time, digital twins help operators monitor performance and predict when a part is likely to fail. Sensors embedded in physical assets stream data to their digital counterparts, allowing engineers to analyze wear, detect anomalies, and schedule maintenance before issues escalate. This reduces unplanned downtime, extends equipment life, and saves millions in repair costs annually making predictive maintenance a top driver of digital twin adoption in industrial settings.
Smarter Infrastructure Management for Cities and Utilities
Urban planners and infrastructure providers are turning to digital twins to better manage complex systems like roads, bridges, utilities, and water networks. These virtual models integrate geographic data, traffic patterns, environmental sensors, and more to help simulate urban behavior. Cities like Singapore and Helsinki have already built full-scale digital twins to monitor real-time conditions, plan upgrades, and assess the environmental impact of development projects. For utility providers, digital twins allow them to detect pressure changes in pipelines, forecast energy consumption, and optimize grid performance with greater accuracy than ever before.
Enhancing Product Design and Development in Engineering
Before a product even hits the market, engineers can use digital twins to simulate how it will behave under real-world conditions. Whether it’s an aircraft component, automotive part, or industrial device, digital models can predict performance, identify design flaws, and reduce the need for physical prototypes. This accelerates the development process and results in better products with fewer costly redesigns. Companies like Siemens, GE, and Airbus use digital twins to refine their R&D processes, reduce time to market, and improve overall product quality by validating every design element in a virtual environment.
Real-Time Operations Optimization in Supply Chains
Supply chains are increasingly dynamic and global, making them ideal candidates for digital twin integration. With a digital twin of the entire supply chain from procurement to production to distribution companies can simulate disruptions, reroute logistics, and balance demand in real time. By continuously feeding live data into the model, businesses gain full visibility into inventory, transportation timelines, and supplier performance. This level of insight allows for faster decision-making, reduced waste, and increased resilience during global or local disruptions something increasingly critical in today’s volatile markets.
Personalized Patient Care and Asset Tracking in Healthcare
In healthcare, digital twins are being developed to model everything from hospital equipment and facility operations to individual patient profiles. For instance, medical devices can have twins that alert technicians to performance issues or calibration needs. More innovatively, digital twins of patients based on imaging, genetic data, and health records are used to simulate treatment responses and personalize care. Hospitals are also using twins to optimize room allocation, staff flow, and emergency preparedness. As this technology evolves, it could play a key role in predictive diagnostics, surgical planning, and remote patient monitoring.
FAQs
Is digital twin technology expensive to implement?
Costs can vary depending on scale and complexity, but modular platforms and cloud-based tools are making digital twins more accessible across industries.
Can small businesses benefit from digital twin technology?
Yes. Even small operations can use scaled-down digital twins for specific assets, such as machinery or inventory systems, to improve efficiency.
Is real-time data required for digital twins to function?
While real-time data enhances accuracy, some twins operate on scheduled data inputs or simulations, depending on the application’s needs.
What’s the difference between a digital twin and a simulation?
Simulations are static and scenario-based, while digital twins are dynamic, continuously updated models reflecting real-time conditions.
Are digital twins secure from cyber threats?
Security is a concern, especially with IoT integration. Robust encryption, access controls, and regular audits are essential to protect twin systems.